
Subscribe to receive the latest blog posts to your inbox every week.
By subscribing you agree to with our Privacy Policy.
E-Commerce has broken the political borders and offers products & services across different country borders. This has resulted in a high volume of cross-border goods and payment flows.
Cross border payments have become an integral part of the day-to-day activities of global businesses. Small Businesses’ zeal to expand their business beyond their country boundaries has been well supported by ongoing digitalisation and high-end technological capabilities across multiple sectors and industries. However, it continues to face significant challenges owing to complicated cross-border mechanisms. The Small businesses face challenges in making or receiving payments internationally because of dealing in different currencies and country specific rules and regulations for international payments. This has created a need for a more agile and frictionless cross border payment framework making cross-border payments as simple as domestic transactions.
Cross-border payments are defined when both the parties i.e. buyer and sellers involved in the transaction are registered in different countries. Most popular cross border payments methods are wire transfer, credit cards and alternative payment methods- mobile wallet, low value payment method. All interaction for payments happens between buyers and sellers through their respective Banks. The Banks communicate with each other through the SWIFT mechanism when it comes to international transactions.
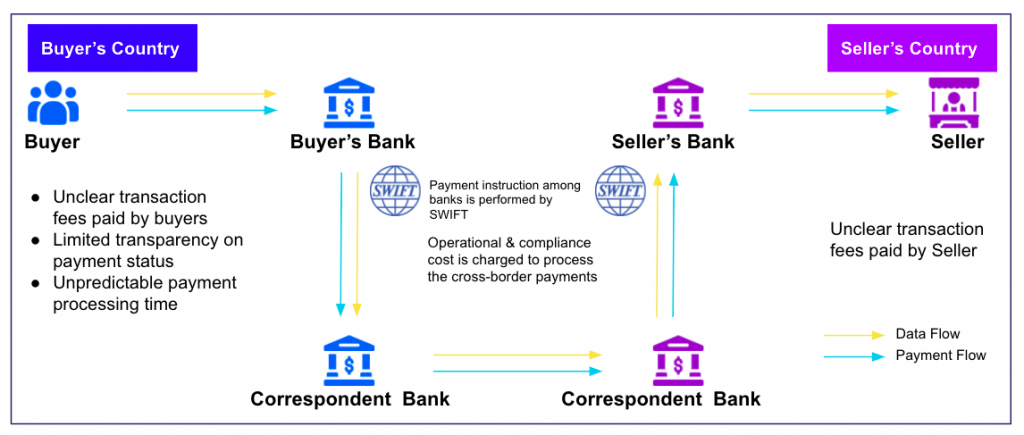
In traditional cross-border payments of correspondent banks, the number of intermediary banks depends on the relationship of the buyer’s and seller bank’s with the correspondent bank. As the number of intermediary banks increases, costs associated with fees and commissions also increase. A Bank can track the transactions till its immediate bank. It becomes difficult for the originating bank to track the transaction once the payment goes to the next bank in the sequence. There is no standard procedure for cross-border payments due to different rules and regulations of each country. Evolving customer requirements, instantaneous fund transfer, cost reduction, complete transparency and technological innovation has initiated the process to improve cross-border payments as a whole.
When a customer makes a purchase, there’s a complete back-end process wherein money gets transferred from the buyer’s bank account to the seller’s bank account. This process becomes very complex when it comes to cross-border payments. In international transactions, currency exchange rates and foreign transaction fees are also involved along with the fees or commission charged by the different bank in the value-chain. In cross border payments domestic and international financial institutions are working together to make the transfer of funds.
When a purchase is made, if the buyer’s and seller’s bank have a direct relationship payment is done very easily and seamlessly but in the absence of direct relationship intermediary bank’s role becomes important. These intermediary banks are called correspondent banks.
Major Banks across the globe have their own branch or correspondent bank’s branch in another city. In such cases, the funds will first move from the Buyer’s bank branch to the Bank’s own branch or its Correspondent bank’s branch in the seller’s country. This fund is further transferred to the seller’s bank who will then credit the seller’s account. There are many entities, different currencies, exchange rates and transaction fees involved in the single international transaction which make the process slow and opaque in nature. The more the number of correspondent banks in the chain, cost and complexity of transaction keeps on increasing.
In the Era of Globalised Digital Economy, international payments still felt backward and analogue.
The future of cross-border payments is clear wherein the world requires ability to move funds instantaneously, seamlessly with full transparency and 24*7 access. As the payment industry started moving forward on this journey, an array of new industry initiatives and emerging technologies are transforming the payments process. Fintechs using emerging technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence, machine learning have started offering faster, agile and seamless solutions to the financial institutions to cater the emerging needs of customers.
Currently multiple paths are being used by the payment service providers such as Real-time payments, SWIFT gpi, SWIFT’s transaction manager, artificial intelligence, blockchain and digital currencies- cryptocurrency, central bank digital currency and stable coins. These new ways in cross-border payments would provide opportunities to make cross-border transactions faster, more frictionless, efficient, transparent and cost-effective like domestic transactions. Fintechs act as catalysts for innovation and bring global payments together through various approaches. Banks have started collaborating with fintech to mend their strengths and optimise their offerings by enhancing the payments infrastructure with latest technologies.
This revolution will transform the landscape of cross-border payments and empower the end user with full control on sending and receiving international payments at any point in time with complete transparency related to fees/ commissions charged and traceability of transactions in the system.
As per Deloitte report – B2B and P2P payments with blockchain would result in a 40% to 80% reduction in transaction costs and take an average of four to six seconds to finalize (compared to two to three days using the standard transfer process).
To know more about our offerings connect with our experts
 In Traditional cross-border payments of correspondent banks, the number of intermediary banks depends on the relationship of the buyer’s and seller bank’s with the correspondent bank. As the number of intermediary banks increases, costs associated with fees and commissions also increase. A Bank can track the transactions till its immediate bank. It becomes difficult for the originating bank to track the transaction once the payment goes to the next bank in the sequence. There is no standard procedure for cross-border payments due to different rules and regulations of each country. Evolving customer requirements, instantaneous fund transfer, cost reduction, complete transparency and technological innovation has initiated the process to improve cross-border payments as a whole.
In Traditional cross-border payments of correspondent banks, the number of intermediary banks depends on the relationship of the buyer’s and seller bank’s with the correspondent bank. As the number of intermediary banks increases, costs associated with fees and commissions also increase. A Bank can track the transactions till its immediate bank. It becomes difficult for the originating bank to track the transaction once the payment goes to the next bank in the sequence. There is no standard procedure for cross-border payments due to different rules and regulations of each country. Evolving customer requirements, instantaneous fund transfer, cost reduction, complete transparency and technological innovation has initiated the process to improve cross-border payments as a whole.
Sales: sales@card91.io
HR: careers@card91.io
Media: comms@card91.io
Support: support@card91.io