Introduction of Blockchain in Fintech
Fintech being a leading light of the startup ecosystem over the years, has played crucial roles in development of the financial services industry. Strong ecosystem level changes are opening up opportunities for new business models. Introduction of blockchain technology in this evolving sector has a considerable impact and advantage.
Blockchain technology is a “chain of blocks” where each block holds timestamped digital data and it’s own previous blocks’ unique identity. The unique features of blockchain have potential to benefit the financial sector significantly.
In this blog we will cover following topics:
- What is Blockchain?
- How Blockchain is transforming the financial ecosystem
- Fintech and Blockchain-Use Cases
- Future of Blockchain in Finance
What is Blockchain technology and its features?
Blockchain is a decentralized database management system. The name signifies itself, a series of blocks containing transaction data, a hash identity, and node details are connected to form a chain. Blockchain is distributed ledger technology (DLT) which allows data to be stored globally on thousands of servers.
Below are the key features of Blockchain for its deeper understanding:
-
Security and Transparency
Financial services all across the world are still centralized and multi-folded. Financial data is mostly stored in centralized databases, and it has to go through multiple intermediaries like front-back offices etc which results in lack of transparency across the system, wherein safety being solely dependent on intermediaries and their level of security.
This lack of transparency within the system fosters security threats or data breaches across the organization.
With the introduction of blockchain technology, transparency and security can be ensured simultaneously. Its distributed consensus based architecture facilitates the security towards data breaches, security threats etc.
-
Privacy
Blockchain system provides operable keys-a public one and a private key. Public key is available to all users in the network. However, the private key is only accessible to the stakeholders of the transaction. This enables transparency wherein the transaction will be visible to all users in the network with public key whereas the stakeholders and the transaction details will only be visible to those who have access to the private key. This process enables transparency within the system while securing the confidential information of the stakeholders.
How does Blockchain work?
Blockchain records validate and store the data in its database. So, it leverages to validate a transaction happening across the network. Each block in the block chain contains follow information
- A hash pointer (link to previous block)
- A timestamp
- Transaction data

Future of Blockchain in Fintech Technology
Andy Martin, a world-class blockchain expert, recently forecasted market changes based on the token economics forced by blockchain and described what exactly it provides:
“Decentralized communities provide certainty of identity, “who am I dealing with”, the certainty of provenance, “what am I buying” and smart contracts give certainty of execution, “if I do this, then I get paid” in these new marketplaces.”
Let’s understand better how Fintech and Blockchain can be chained together to build a FinBlock ecosystem.
Blockchain in the fintech industry can provide us a more seamless and effective way to banking, built around concepts of equity and decentralization. Blockchain-based fintech enables seamless transfer of funds, top of the line security and transparent financial tracking.
Reduced Costs and Transactions in Minutes
With blockchain integration in fintech applications, sending money, regardless of the amount, is much faster. Blockchain-based transactions occur in real time, so the recipient will not have to wait for days or weeks to get the money.
In addition to this, fintech applications powered by blockchain technology can drastically reduce the transaction costs enabling direct, P2P transactions that eliminate any middleman, meaning all unnecessary expenses and fees.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Fintech
Some use cases of blockchain in fintech services are: Cross Border Payments, Lending Platforms, Credit Score, Invoice Management and Billing Solution, Fund Investment, Government Expenses, Financial Record Keeping, Stock Exchange and Initial Public Offering
Let’s discuss Cross Border Payments and Lending Platforms use case in details:
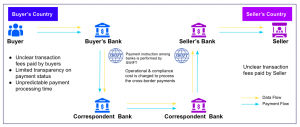
Cross-Border Payments
Banks always charge an additional fee for every transfer or payments across borders, which in a way becomes expensive and slow.
E.g If you want to transfer money from India to the USA, the transfer goes through one or more financial institutions before it reaches the receiver.
Introduction of Blockchain allows individuals to send and receive money with minimum interference of different intermediaries, which enhances the payment settlement quickly and efficiently.
Lending Platforms
When it comes to lending, one is required to establish trust and make a transaction happen. However, with blockchain technology in fintech, borrowers can directly deal with the lenders on the rate of interest, installments, and duration of the transaction with the help of immutable smart contracts.
Conclusion:
Blockchain in financial services can offer multiple benefits, which can help transform the finance industry. According to KPMG, “blockchain can reduce errors by up to 95%, increase efficiency by 40% and reduce capital consumption by up to 75%”. Blockchain in finance is an exciting concept with the potential to transform the finance industry.
Blockchain can help different financial institutions and government entities to improve trust, bring transparency and cut down costs.